At Google I/O 2024, the company announced several key updates for Google Play that are particularly relevant for developers in the mobile app subscription space. These updates are designed to help developers optimize subscription models, improve user retention, and enhance security. Let’s look at those updates that will be the most useful for app subscription growth.
Refreshed Play Store UI and Engage SDK
A lot of focus on the presentation was put on fresh ways of engaging users. First, Google presented a new more engaging user interface of the Play Store that provides more surfaces for promo content from your apps.

The surfaces work in two ways:
- Showcase features and content from the already installed apps to re-engage the user. In this case, developers can use deep links to guide the user to check a certain piece of content or make a purchase right in the app.
- Present the user with promo materials from the not-yet-installed apps. For these purposes, the surfaces may still display certain app features, content, and offers.
Surfaces are on-device generated, meaning they are organized exclusively for each user depending on their interests and behavior.

This brand new approach becomes possible after integrating Engage SDK which currently is not available to everyone, but you can try to get access by joining the developer preview. By tailoring experiences based on user preferences and behaviors, such a feature can significantly boost user engagement and improve app retention rates.
Expanded payment options
To increase global reach, Google Play has introduced new payment options, making it easier for users worldwide to subscribe to apps. A huge amount of attention is paid to collaboration with local banks and payment providers.

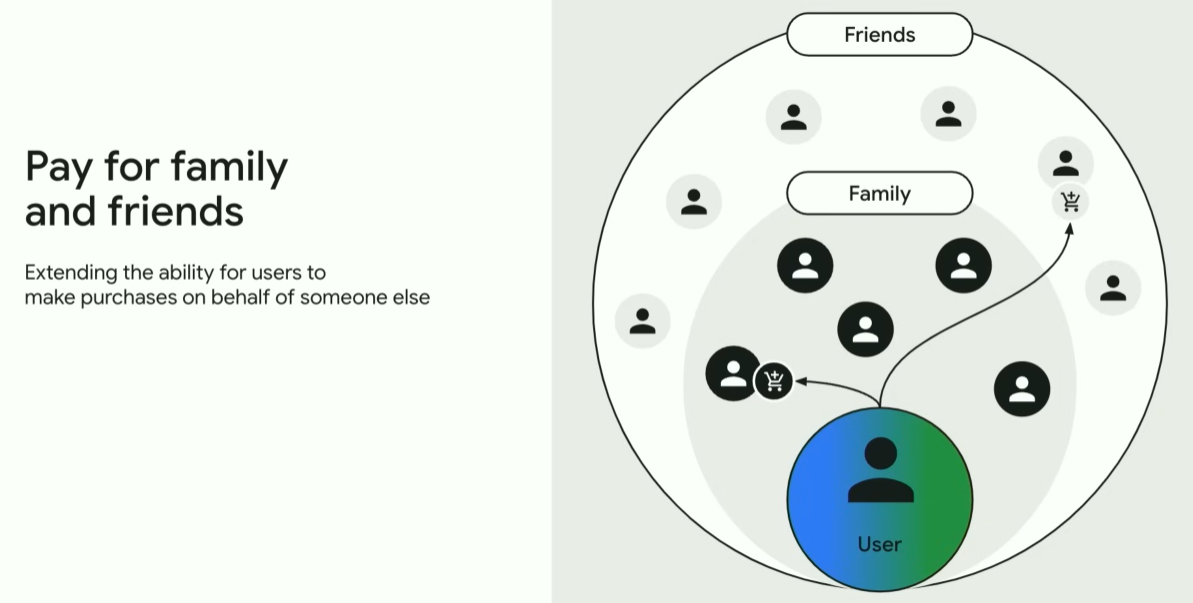
Apart from the usual family sharing, Google has also introduced the ability to pay for family members and friends at their request. The user can now choose the option of asking someone else to pay and then share the generated payment link with any person. This option is currently available only on the Indian market and requires Billing Library 6.0 or higher. It’s too early to say how this feature can affect the revenue situation of a particular app when it gets scaled (if it ever does), but it seems like an interesting option to test on your paywall.
Optimized pricing strategies
Google Play now offers optimized pricing strategies, enabling developers to test different pricing models and identify the most effective approach for their target audience. One of the notable features is the automatic update of the user price ranges that reflects the currency fluctuations against the US dollar.
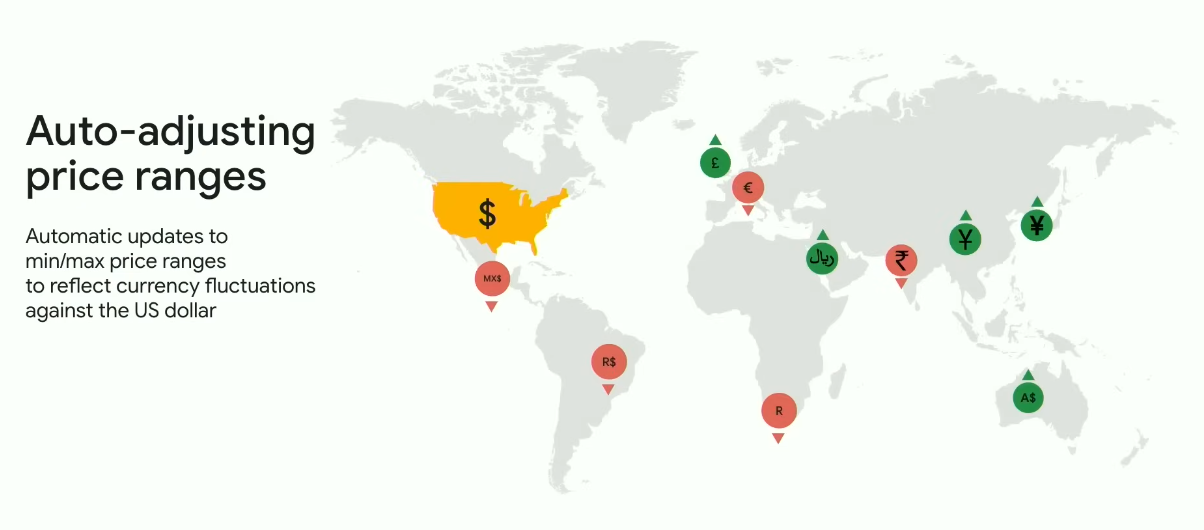
Another “pivotal” update is the increased pricing flexibility with the ability to price your products as high as $999.99. Google suggests that such flexibility should open new horizons for offering ultra-premium experience. Though still not premium enough compared to the App Store’s limit of $9,999.99.

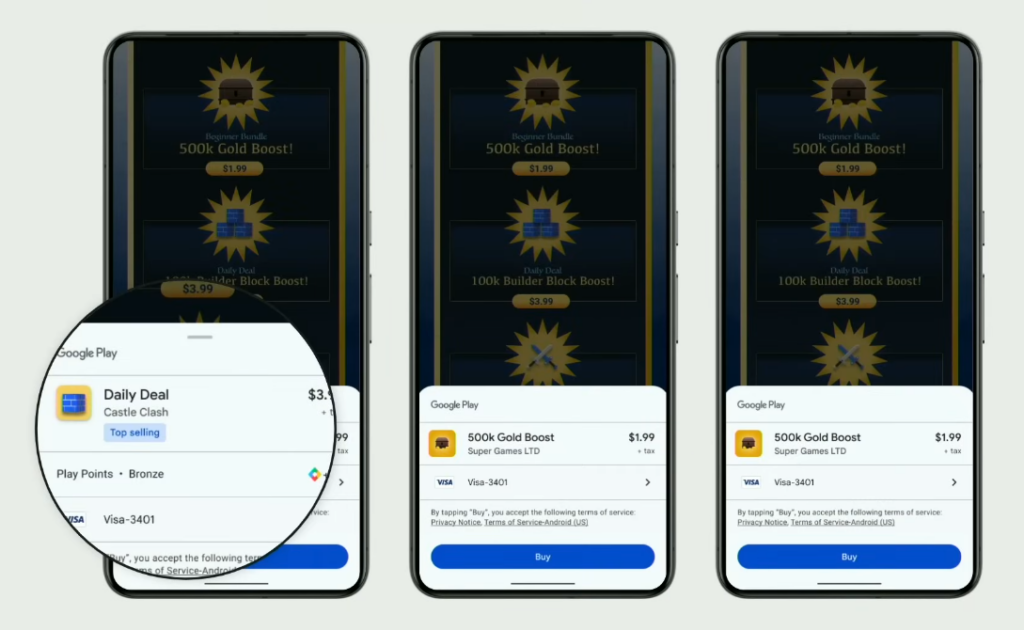
Expanded badges
Google Play can now encourage customers to complete a purchase by showing how products are trending with the help of new badges, such as Trending, Popular, and Best-selling. However, it’s unclear how exactly such badges will be assigned to products and what the threshold for earning them is.
Installment subscriptions
Probably one of the most notable updates concerns the ability to pay for subscriptions by installment. It’s worth noting, however, that it’s not an option on the user side, it’s a developer-provided feature. This means that users will only be able to choose installment payments if the developer has configured their subscription model to support this payment method. If the option is provided, the user can divide the payment for a subscription into several monthly payments, e.g. provide 12 monthly payments for an annual subscription.
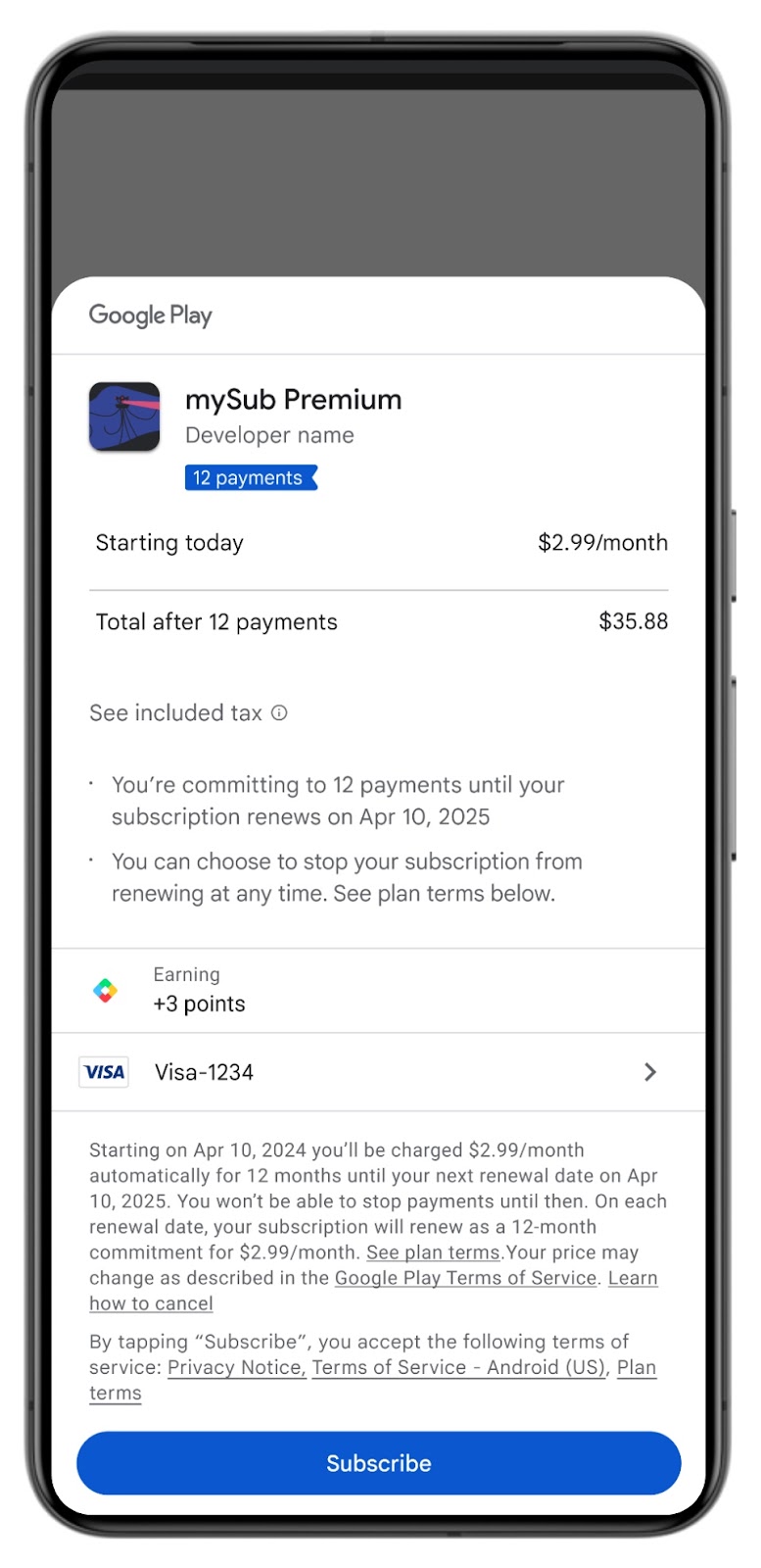
There are 3 main aspects to note here:
- All installment subscriptions are paid in monthly intervals; users and developers cannot adjust the frequency or timing of payments.
- Developer payouts will happen as users make their monthly payments.
- Developers are not paid upfront when the user signs up for the subscription.
From the looks of it, such an approach is basically a variation of an ordinary monthly subscription, at least from the revenue-generating perspective. Although it may be potentially more profitable in the long run as paying for an annual subscription should keep people more engaged with the product, thus increasing LTV and retention rates.
Might be a good idea to test “a monthly subscription” vs “an annual by installments” on your paywall to see which one will look more appealing to the user. The option is currently available only for Brazil, France, Italy, and Spain.
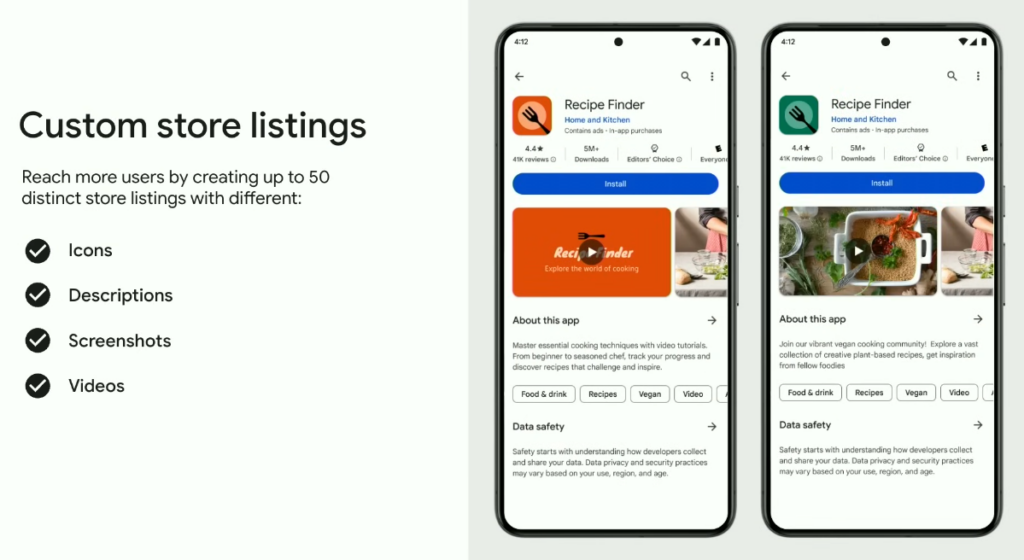
Custom store listings
Google Play developers can now create up to 50 different store listings that will feature different icons, descriptions, screenshots, and videos. Tailoring your app page for different audience segments will provide the best first impression and should significantly increase user acquisition rates.
Play Market allows targeting custom store listings by Country, Pre-registration status, Deep links, Inactive users, Google Ads campaign, and Search keywords. Basing custom store pages on the keywords for your app’s features and benefits is likely to attract the right audience.
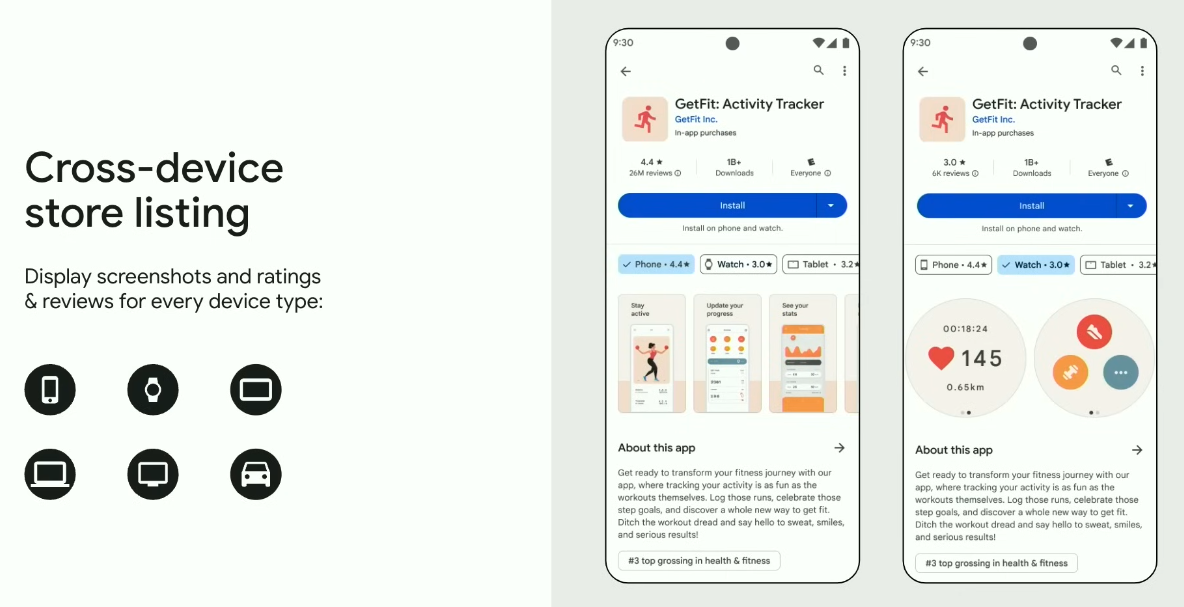
Worth pointing out that you can customize your store listings for every device type, including tablets, watches, Chromebooks, and more. Your store listing will now feature screenshots along with ratings and reviews that are tailored to each form factor, providing users on various devices with a clearer understanding of the app experience they can expect. Additionally, incorporating device-specific details will enhance your app’s discoverability for users who search by device type or explore a newly dedicated page for other devices.
Deep links patching
A small yet valuable update concerns the use of deep links. To make managing deep links even more efficient, Google introduced deep links patching in Play Console. This feature enables experimenting with or quickly modifying the deep-link setup without needing to release a new app version.
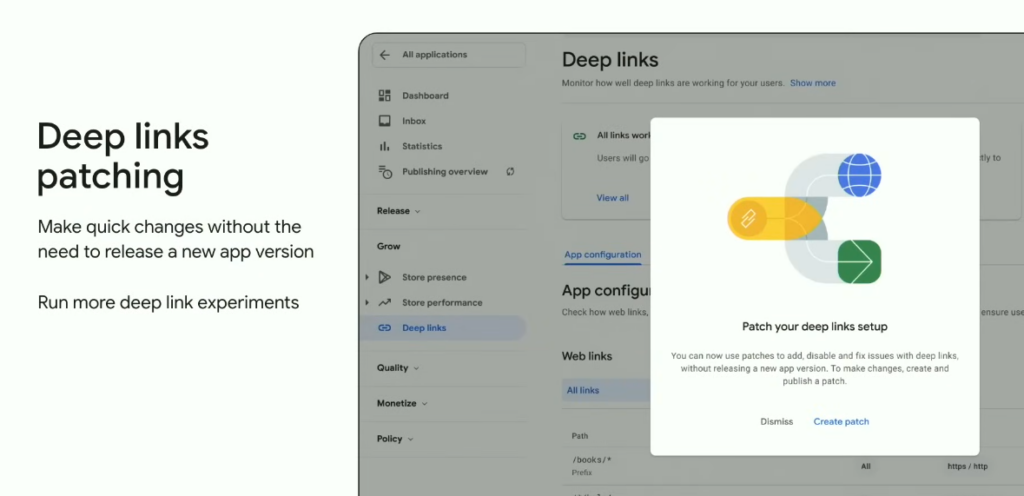
The changes made are not permanent unless you decide to keep them. After making the changes, you can review them by previewing or downloading a test version on your device. If everything works as expected, you can push the patch live, and Google Play will update the changes for your users.
Orders API
Orders API is a tool provided by Google that allows developers to manage and query orders for in-app purchases and subscriptions. Developers can use it to retrieve details about in-app purchases and subscriptions, including the status of an order, purchase time, and SKU details.

The API also allows developers to process refunds and cancellations of orders directly. The API is still in the early access program, so we can’t yet draw any conclusions on how it operates or how convenient it is. In the meantime, you can use Adapty to get detailed real-time mobile analytics that presents all the aforementioned data in convenient dashboards and charts.
Play Billing Lab
The Play Billing Lab app is a specialized tool developed by Google for Android developers to test and verify their Play Billing Library integrations. This app is particularly useful for ensuring that in-app purchases and subscription functionalities are working correctly before releasing updates or new features to the public.
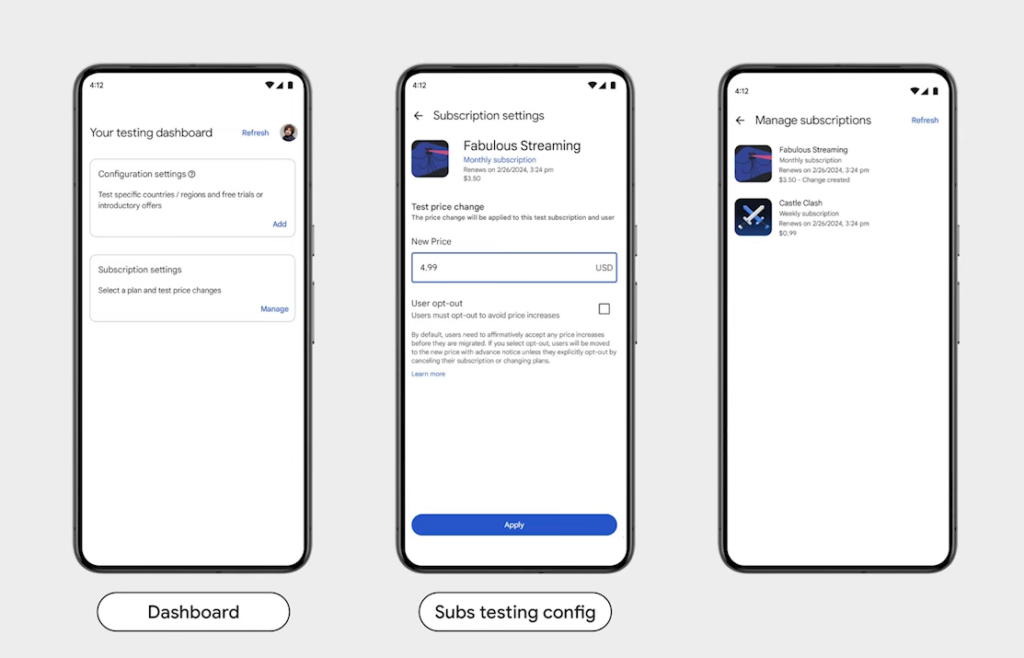
The app allows developers to sign in with a licensed testing account and simulate the purchase flow. This includes testing in-app purchases, subscriptions, and various billing scenarios without needing to use real payment methods. It’s always great to have more ways to test different aspects of your app before releasing or updating it.
How useful are these updates?
It’s safe to say that the updates announced at Google I/O 2024 for Google Play should help developers better manage subscriptions, optimize revenue, and engage with users. By leveraging the new features, developers can create a more compelling and user-friendly subscription experience.
However, we saw nothing revolutionary – just a few small (and even experimental) steps to consolidate the Android ecosystem and keep the Play Market in better shape. Updates like the Play Billing Lab or Custom store listings will undoubtedly be useful for developers but at the same time should bring more order to the store itself.
Most of these updates and features aren’t out yet and will be available with the release of Play Billing Library 7.0. With Adapty you don’t have to worry about Billing Library updates or deprecations – we aim to support the 7.0 version as fast as possible and provide our users with all the latest features.
There are more Play Market updates that didn’t make our highlights but may be worth checking out, so you can visit the Android Developers Blog to see the full presentation.