应用内购买(In-app purchase)是最受欢迎的应用盈利方式,尤其是订阅(subscription)。一方面,订阅可以让开发者投资开发内容和产品,另一方面,它也可以帮助用户获得更高质量的应用程序(APP)。应用内购买需支付30%的佣金,但如果用户订阅超过一年或应用每年的收入低于一百万美元,则佣金为15%。
在本文中,我们将解释如何:
- 在Google Play控制台中创建一个产品;
- 配置订阅:如何明确持续时间、价格、试用(trial);
- 在应用程序中添加产品列表。
创建订阅
在我们开始之前,请确保您:
- 拥有Google Play的开发者账号。
- 已经签署了所有协议,并准备开始工作。
现在,让我们进入正题,创造我们的第一个产品吧。
切换到您的开发者账户并选择应用程序。
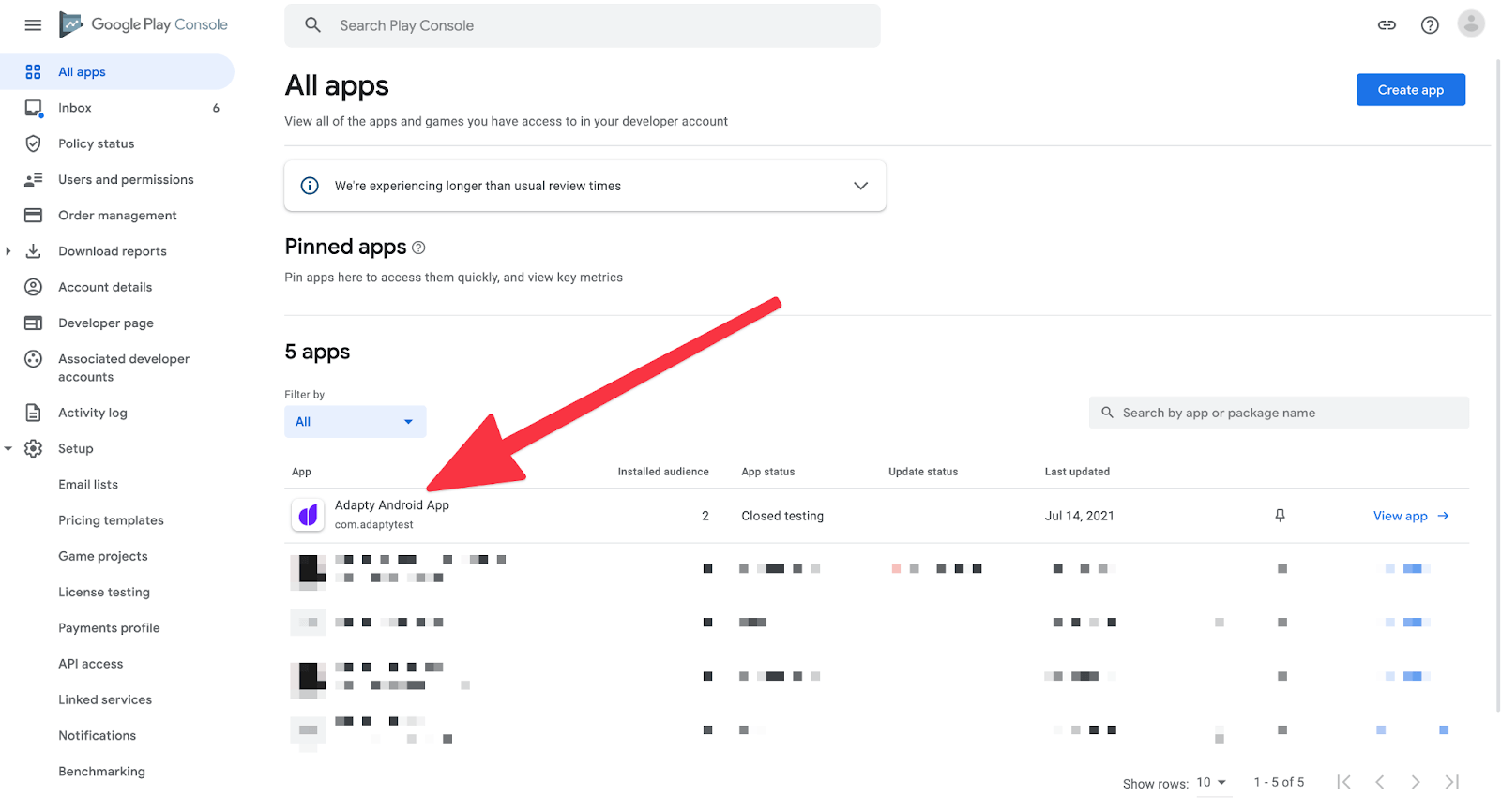
然后,在左侧的菜单中找到“Products”部分,选择“Subscriptions”并点击“Create a Subscription”。
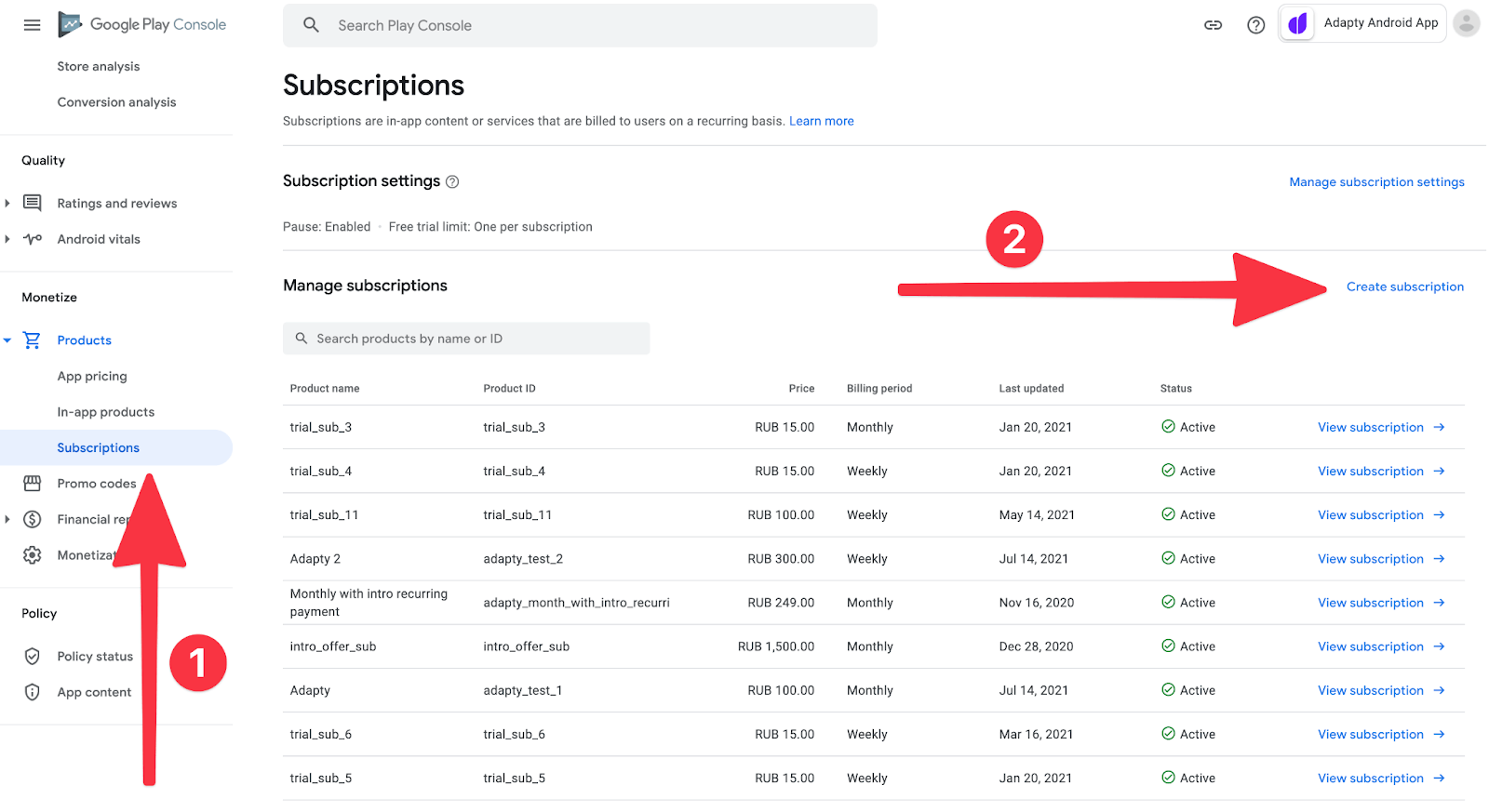
然后,我们就会看到订阅配置器。这里有一些要点。
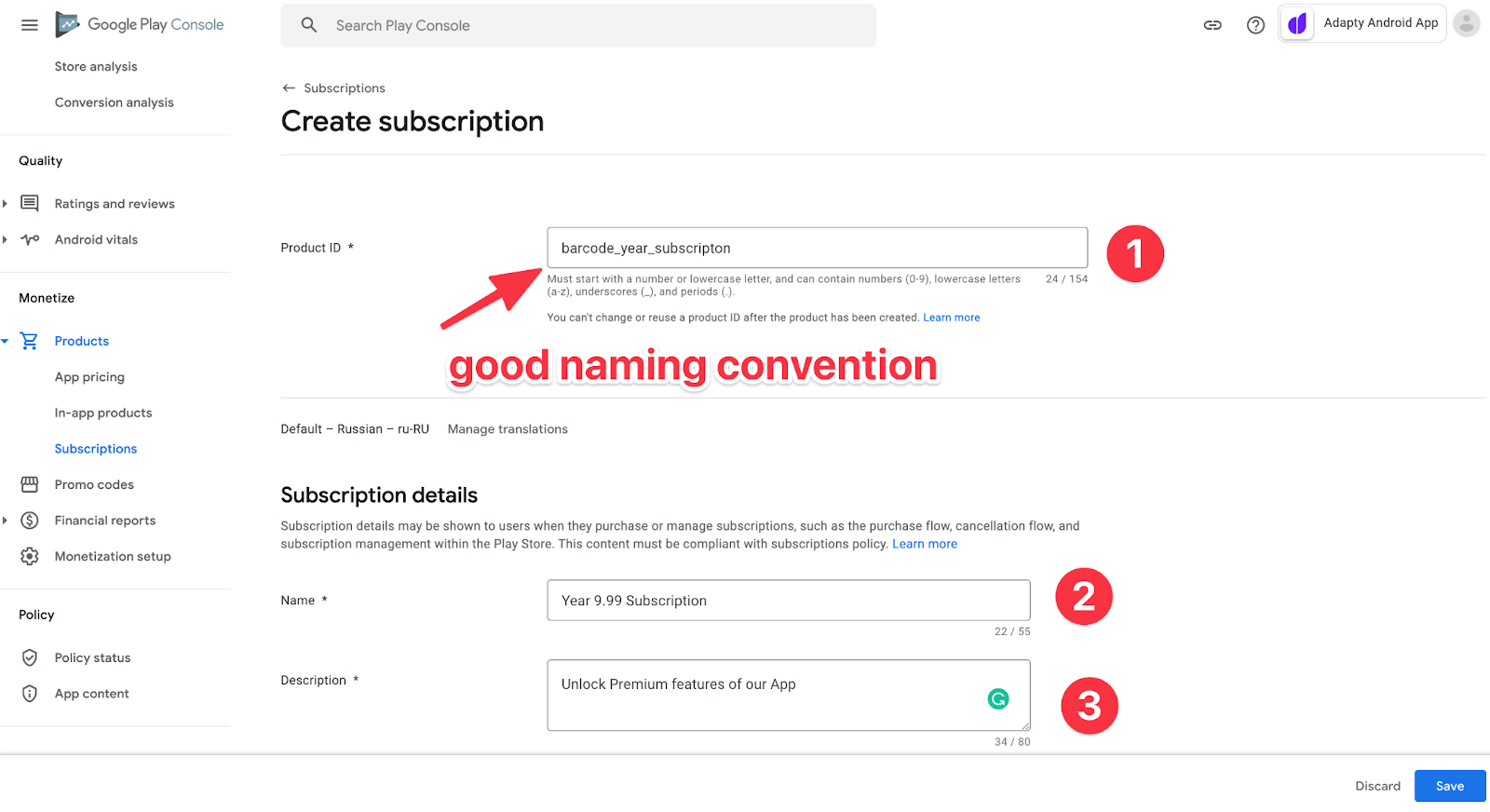
- 创建将在应用程序中使用的ID。在ID中添加订阅期或其他有用信息是个好主意,这样就可以创建一种样式的产品,让分析销售统计数据更容易。
- 用户将在商店中看到的订阅名称。
- 订阅描述。用户也会看到。
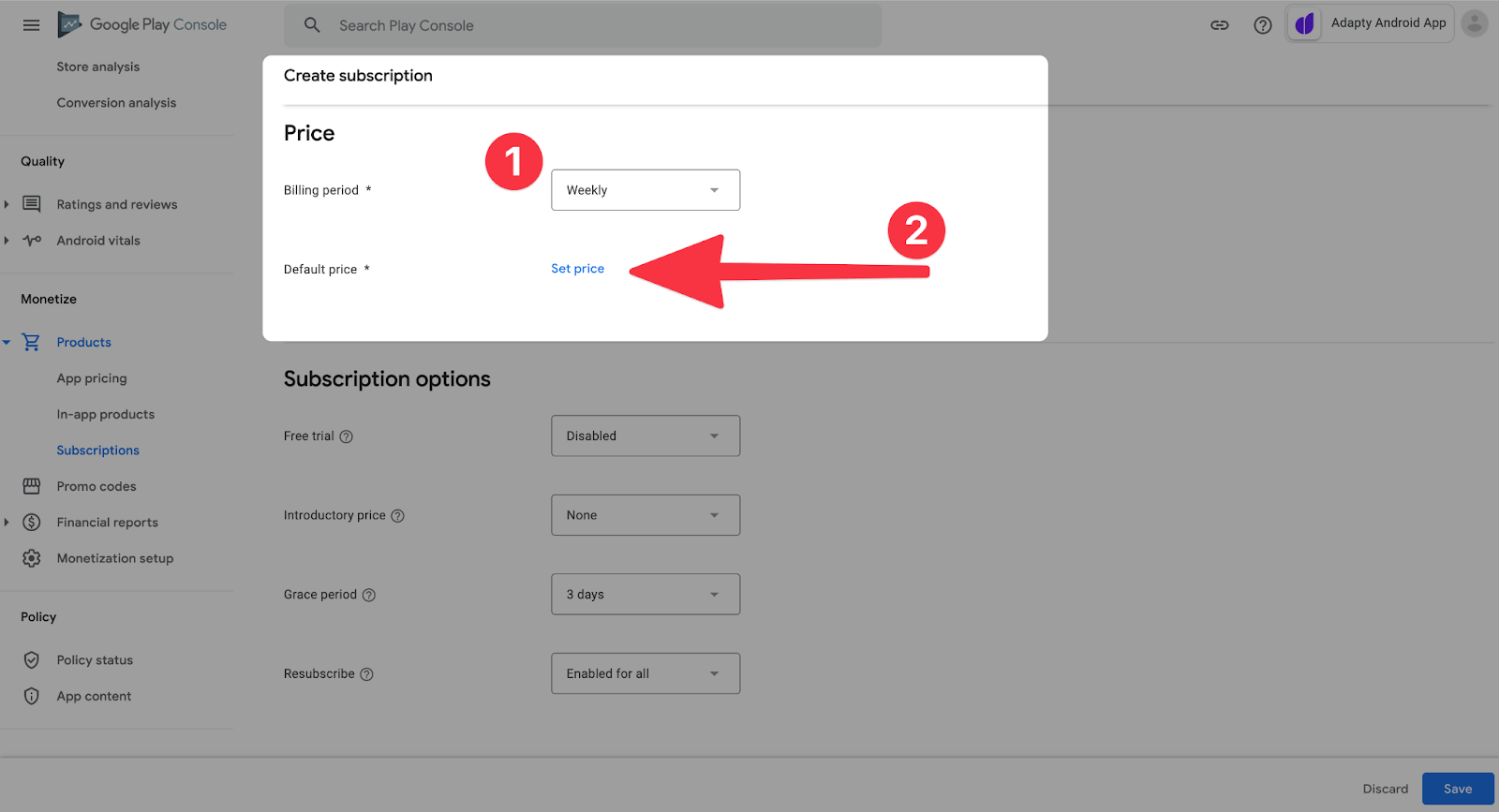
向下滚动并选择订阅期。在我们这里,是一周。设定价格。
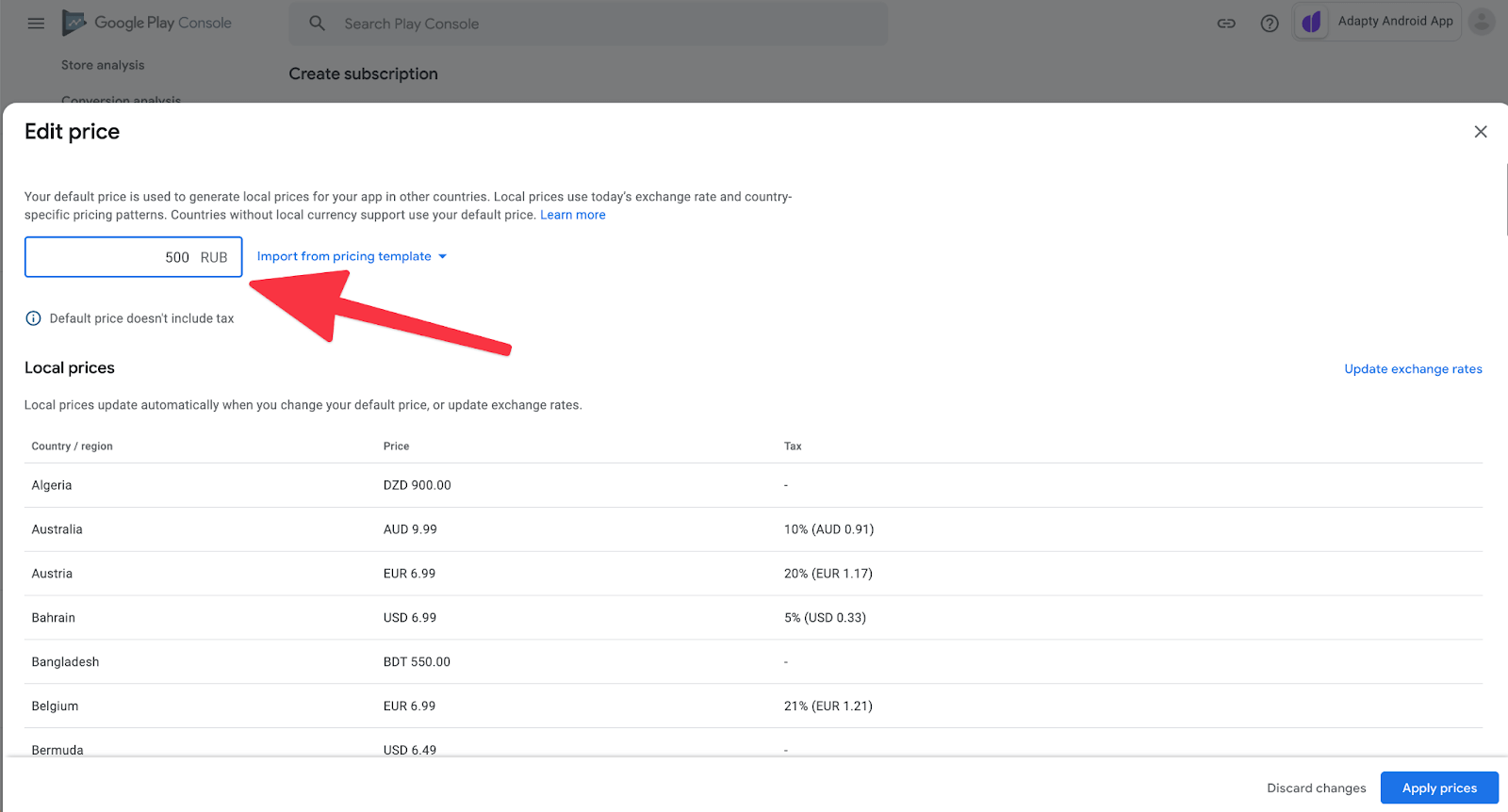
通常,您用基本账户货币设置价格,系统会自动转换价格,但是您也可以手动编辑特定国家的价格。
请注意Google显示了每个国家的税收。这很好,但App Store Connect没有做到这一点。
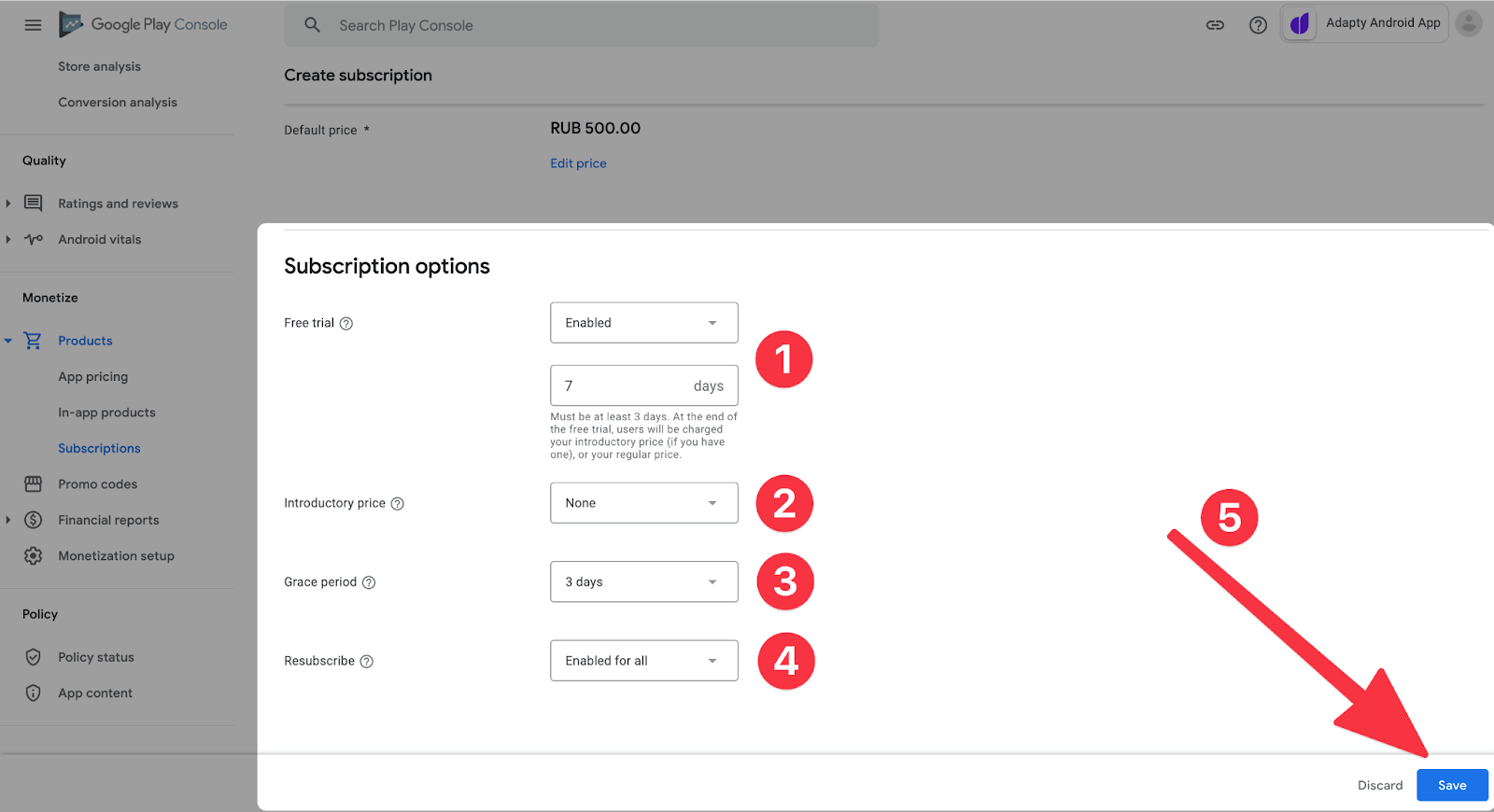
向下滚动并选择(如果需要):
- 免费试用期。
- 推介价格,这是第一次付款期的价格。
- 宽限期。如果用户有支付问题,您仍然可以为他们提供几天的高级访问。
- 取消订阅后,有机会从应用商店重新订阅,而不是从应用程序。
比较Play Console和App Store Connect中的购买过程
尽管iOS平台上的订阅模式能更有效地实现盈利,但Play Console的管理委员会更方便、更有组织性、本地化也更好,而且运行速度也更快。
产品创造的过程尽可能简单。在这里,我们讲述了如何在iOS上创建产品。
在应用程序中添加产品列表
一旦创建了产品,我们就可以研究用于接受和处理购买的架构。一般来说,过程是这样的:
- 添加Billing Library。
- 开发一个与Google Play产品交互的类。
- 执行所有处理购买的方法。
- 添加购买的服务器验证。
- 收集分析。
在这一部分中,让我们仔细看看前两点。
向项目添加Billing Library:
implementation "com.android.billingclient:billing:4.0.0"在编写时,最新版本是4.0.0。您可以随时用任何其他版本替换它。
让我们创建一个会覆盖与Google Play的交互逻辑的包装器类,并从其中的Billing Library初始化BillingClient。我们将这个类称为BillingClientWrapper。
这个类将实现PurchasesUpdatedListener接口。我们现在将为它重写一个方法——onPurchasesUpdated(billingResult: BillingResult, purchaseList: MutableList<Purchase>?)——在购买后立即需要这个,但我们将在下一篇文章中描述实现过程。
import android.content.Context import com.android.billingclient.api.* class BillingClientWrapper(context: Context) : PurchasesUpdatedListener { private val billingClient = BillingClient .newBuilder(context) .enablePendingPurchases() .setListener(this) .build() override fun onPurchasesUpdated(billingResult: BillingResult, purchaseList: MutableList<Purchase>?) { // here come callbacks about new purchases } }Google建议避免BillingClient和Google Play之间有多个活跃连接,以防止多次执行购买的回调操作。因此,在一个单例类中应该有一个惟一的BillingClient。这个例子中的类不是单例的,但是我们可以通过这种方式使用依赖注入(例如,在Dagger或Koin的帮助下),只允许一个实例在单个时间点存在。
如需使用Billing Library发出任何请求,BillingClient在发出请求时必须与Google Play有一个活跃连接,但在某些时刻连接可能会丢失。为了方便起见,让我们编写一个包装器,这让我们可以仅在连接处于活跃状态时发出任何请求。
为了获得产品,我们需要他们在市场上的ID。但这对一个请求来说是不够的,我们还需要产品类型(订阅或一次性购买),这就是为什么我们可以通过“组合”两个请求的结果来获得产品的一般列表。
对产品的请求是异步的,因此我们需要一个回调,它要么为我们提供产品列表,要么返回一个错误模型。当发生错误时,Billing Library会返回它的一个BillingResponseCodes,以及debugMessage。让我们为错误创建回调接口和模型:
interface OnQueryProductsListener { fun onSuccess(products: List < SkuDetails > ) fun onFailure(error: Error) } class Error(val responseCode: Int, val debugMessage: String)下面是用于获取特定类型产品数据的私有方法的代码,以及用于“组合”两个请求的结果并向用户提供最终产品列表或显示错误消息的公共方法的代码。
fun queryProducts(listener: OnQueryProductsListener) { val skusList = listOf("premium_sub_month", "premium_sub_year", "some_inapp") queryProductsForType( skusList, BillingClient.SkuType.SUBS ) { billingResult, skuDetailsList -> if (billingResult.responseCode == BillingClient.BillingResponseCode.OK) { val products = skuDetailsList ?: mutableListOf() queryProductsForType( skusList, BillingClient.SkuType.INAPP ) { billingResult, skuDetailsList -> if (billingResult.responseCode == BillingClient.BillingResponseCode.OK) { products.addAll(skuDetailsList ?: listOf()) listener.onSuccess(products) } else { listener.onFailure( Error(billingResult.responseCode, billingResult.debugMessage) ) } } } else { listener.onFailure( Error(billingResult.responseCode, billingResult.debugMessage) ) } } } private fun queryProductsForType( skusList: List<String>, @BillingClient.SkuType type: String, listener: SkuDetailsResponseListener ) { onConnected { billingClient.querySkuDetailsAsync( SkuDetailsParams.newBuilder().setSkusList(skusList).setType(type).build(), listener ) } }因此,我们获得了有关产品的重要信息(SkuDetails),我们在这可以看到本地化名称、价格、产品类型,以及关于订阅的入门价格和试用期,以及计费周期(如果该用户可用)的信息。最后的类是这样的:
import android.content.Context import com.android.billingclient.api.* class BillingClientWrapper(context: Context) : PurchasesUpdatedListener { interface OnQueryProductsListener { fun onSuccess(products: List<SkuDetails>) fun onFailure(error: Error) } class Error(val responseCode: Int, val debugMessage: String) private val billingClient = BillingClient .newBuilder(context) .enablePendingPurchases() .setListener(this) .build() fun queryProducts(listener: OnQueryProductsListener) { val skusList = listOf("premium_sub_month", "premium_sub_year", "some_inapp") queryProductsForType( skusList, BillingClient.SkuType.SUBS ) { billingResult, skuDetailsList -> if (billingResult.responseCode == BillingClient.BillingResponseCode.OK) { val products = skuDetailsList ?: mutableListOf() queryProductsForType( skusList, BillingClient.SkuType.INAPP ) { billingResult, skuDetailsList -> if (billingResult.responseCode == BillingClient.BillingResponseCode.OK) { products.addAll(skuDetailsList ?: listOf()) listener.onSuccess(products) } else { listener.onFailure( Error(billingResult.responseCode, billingResult.debugMessage) ) } } } else { listener.onFailure( Error(billingResult.responseCode, billingResult.debugMessage) ) } } } private fun queryProductsForType( skusList: List<String>, @BillingClient.SkuType type: String, listener: SkuDetailsResponseListener ) { onConnected { billingClient.querySkuDetailsAsync( SkuDetailsParams.newBuilder().setSkusList(skusList).setType(type).build(), listener ) } } private fun onConnected(block: () -> Unit) { billingClient.startConnection(object : BillingClientStateListener { override fun onBillingSetupFinished(billingResult: BillingResult) { block() } override fun onBillingServiceDisconnected() { // Try to restart the connection on the next request to // Google Play by calling the startConnection() method. } }) } override fun onPurchasesUpdated(billingResult: BillingResult, purchaseList: MutableList<Purchase>?) { // here come callbacks about new purchases } }今天就到这吧。在下一篇文章中,我们将介绍购买实现、测试和错误处理。