Push notifications are short, clickable messages sent directly to a user’s device by mobile apps or websites, even when the app isn’t actively in use. They appear on lock screens, notification centers, and banners to deliver timely updates, promotions, reminders, and alerts. For mobile apps, push notifications are one of the most effective tools for driving user engagement, increasing retention, and re-engaging inactive users.
What are push notifications?
Push notifications are messages initiated by an application server and delivered to a user’s device without requiring any action from the user. Unlike pull-based communication where users must request information, push technology proactively sends alerts to devices that have the app installed and notifications enabled.
These messages can reach users even when their phone is locked or the app isn’t running, making them one of the most direct communication channels available to app publishers. When a push notification arrives, it typically appears as a banner or alert on the device screen, accompanied by a sound or vibration depending on user preferences.
Push notifications were first introduced by Apple in June 2009 with the Apple Push Notification Service (APNs). Google followed in 2010 with Google Cloud to Device Messaging (C2DM), which later evolved into Firebase Cloud Messaging (FCM). Since then, push notifications have become an essential feature for virtually every mobile application.
Key characteristics of push notifications
| Characteristic | Description |
| Delivery method | Server-initiated (push) rather than user-requested (pull) |
| User requirement | App must be installed; user must opt-in (iOS) or not opt-out (Android) |
| Visibility | Appears on lock screen, notification center, and as banners |
| App state | Works even when app is closed or device is locked |
| Content types | Text, images, videos, GIFs, action buttons, sounds |
| Platforms | iOS, Android, web browsers, desktop, wearables |
Why are push notifications important for marketing?
Push notifications have become a cornerstone of mobile marketing strategy due to their ability to reach users directly and instantly. Here’s why they matter:
| Benefit | Description | Business impact |
| Real-time communication | Deliver messages instantly to users | Time-sensitive promotions and alerts reach users immediately |
| High visibility | Appear on lock screen and notification center | 90%+ of push notifications are seen (vs. ~20% email open rates) |
| User engagement | Drive users back to your app | Apps using push see 88% higher engagement |
| Retention improvement | Re-engage inactive users | 3x higher retention for users receiving push in first 90 days |
| Cost efficiency | No per-message cost (unlike SMS) | Free delivery to unlimited users |
| Personalization | Target based on behavior and preferences | Personalized push increases CTR by up to 4x |
| Conversion boost | Drive specific actions | Push notifications can increase conversions by 7x |
Push notifications vs. other channels
| Channel | Delivery speed | Cost per message | Open/view rate | Requires app |
| Push Notifications | Instant | Free | 50-80% | Yes |
| Minutes to hours | Low | 15-25% | No | |
| SMS | Instant | $0.01-0.05 | 90%+ | No |
| In-App Messages | When app opens | Free | 25-40% | Yes (app must be open) |
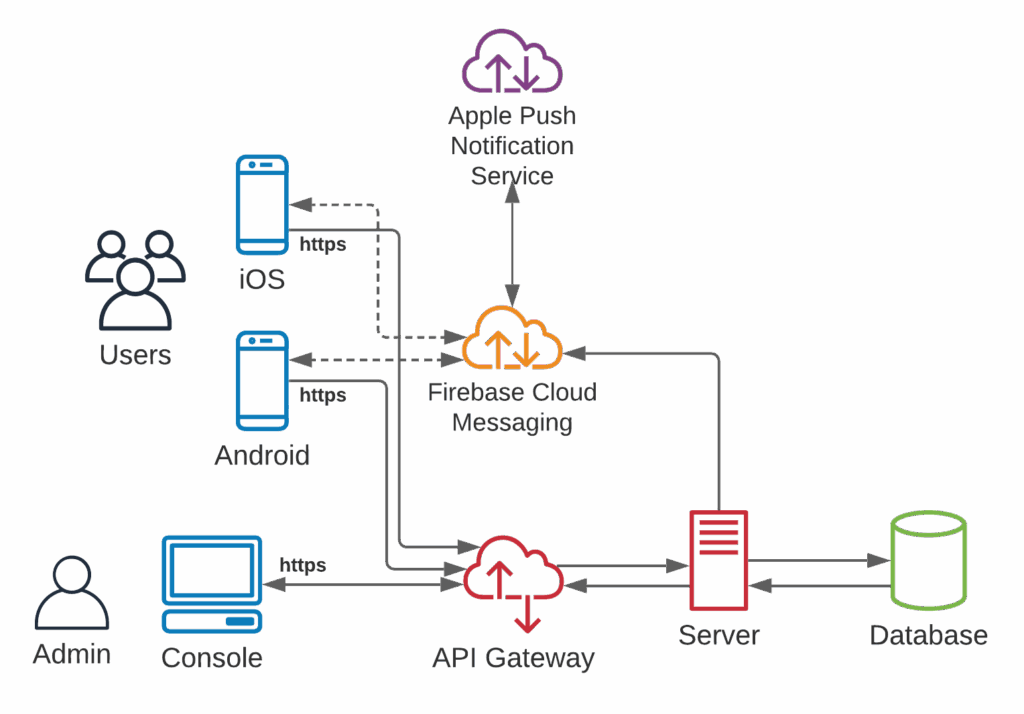
How do push notifications work?
Push notifications follow a specific flow from the app server to the user’s device, facilitated by Operating System Push Notification Services (OSPNS).
Step 1: User installs app and opts in When a user downloads and installs an app, the app registers with the device’s operating system push notification service (APNs for iOS, FCM for Android). The user must grant permission for the app to send notifications.
Step 2: Device token generation Upon registration, the OSPNS generates a unique device token—a specific identifier for that app on that device. This token is sent back to the app and then forwarded to the app publisher’s server.
Step 3: Token storage The app publisher stores the device token in their database, associating it with the user’s profile. This allows them to target specific users or segments with notifications.
Step 4: Message composition When the publisher wants to send a notification, they compose the message through their push notification service or customer engagement platform, defining the content, target audience, and delivery timing.
Step 5: Delivery to OSPNS The message is sent to the appropriate OSPNS (APNs or FCM) along with the target device tokens. The OSPNS validates the request and queues the message for delivery.
Step 6: Notification delivery The OSPNS delivers the notification to the user’s device. The device displays the notification according to the user’s settings and the notification’s configuration.
Step 7: User interaction The user sees the notification and can choose to interact with it (tap to open), dismiss it, or take action using buttons if provided.
What are core types of push notifications?
Push notifications can be categorized based on their purpose and content. Understanding these types helps you craft the right message for each situation.
1. Transactional notifications
Transactional push notifications are triggered by specific user actions or system events. They provide essential information users expect and need, such as order confirmations, shipping updates, payment receipts, or appointment reminders. These notifications reduce friction in the user experience by keeping customers informed about important activities related to their account or purchases.
Examples: Order shipped, payment confirmed, password reset, booking confirmation, account security alerts.
2. Promotional notifications
Promotional (or marketing) notifications are designed to drive engagement, sales, and revenue. They inform users about sales, discounts, new products, or special offers. While effective, promotional notifications must be used thoughtfully to avoid overwhelming users and causing opt-outs.
Examples: Flash sale alerts, new product launches, limited-time offers, loyalty rewards, personalized recommendations.
3. Informational notifications
Informational notifications deliver useful updates that don’t require immediate action but provide value to users. These include news alerts, content updates, feature announcements, or general information relevant to the user’s interests.
Examples: Breaking news, new episode available, app update released, weather alerts, sports scores.
4. Reminder notifications
Reminder notifications help users remember tasks, appointments, or commitments. They’re particularly valuable for productivity apps, healthcare apps, fitness apps, and any service involving scheduled activities.
Examples: Appointment reminder, medication time, workout scheduled, bill due date, subscription renewal.
5. Geolocation-based notifications
These notifications are triggered when users enter or exit specific geographic areas (geofences). They enable highly contextual messaging based on physical location, making them powerful for retail, dining, travel, and local services.
Examples: Store nearby alert, local event notification, airport gate change, restaurant promotion when nearby.
6. Re-engagement notifications
Re-engagement notifications target users who haven’t opened the app in a while. They aim to bring inactive users back through compelling content, special offers, or reminders of what they’re missing.
Examples: “We miss you” messages, streak reminders, abandoned cart alerts, personalized content suggestions.
Industries that use push notifications
Push notifications are valuable across virtually all industries, but some sectors rely on them more heavily due to their need for real-time, actionable communication.
| Industry | Primary use cases | Key venefits |
| E-commerce and retail | Flash sales, abandoned cart recovery, order updates, personalized offers | Higher conversion rates, reduced cart abandonment |
| Banking and finance | Transaction alerts, fraud warnings, payment reminders, account updates | Enhanced security, improved customer trust |
| Media and entertainment | Breaking news, new content alerts, personalized recommendations | Increased content consumption, higher retention |
| Travel and hospitality | Flight updates, gate changes, booking confirmations, check-in reminders | Better travel experience, reduced missed flights |
| Gaming | Daily rewards, event notifications, friend activity, streak reminders | Higher DAU, increased in-app purchases |
| Healthcare and fitness | Medication reminders, appointment alerts, health tips, workout motivation | Better health outcomes, consistent engagement |
| Food and delivery | Order status, delivery tracking, promotions, reorder suggestions | Improved customer experience, repeat orders |
| Social media | Friend requests, messages, mentions, content interactions | Real-time engagement, increased app opens |
| Education | Assignment reminders, grade notifications, course updates, learning streaks | Better completion rates, consistent learning |
| Subscription apps | Renewal reminders, new content, trial expiration, feature updates | Reduced churn, higher LTV |
How are push notifications added to a mobile app?
Implementing push notifications requires technical integration with platform-specific services and often involves third-party providers for enhanced functionality.
| Step | iOS implementation | Android implementation |
| 1. Register with OSPNS | Register with Apple Push Notification Service (APNs) | Register with Firebase Cloud Messaging (FCM) |
| 2. Obtain credentials | Generate APNs authentication key or certificate | Create Firebase project and download config file |
| 3. Integrate SDK | Add APNs framework or third-party SDK | Add FCM SDK or third-party provider SDK |
| 4. Request permission | Call requestAuthorization() to get user consent | Android 13+ requires runtime permission request |
| 5. Handle device token | Implement didRegisterForRemoteNotifications | Implement onNewToken() callback |
| 6. Configure backend | Set up server to communicate with APNs | Set up server to communicate with FCM |
| 7. Test notifications | Use Xcode or APNs sandbox | Use Firebase Console or FCM test message |
Design of an iOS push notification
Understanding the anatomy of a push notification helps you optimize each element for maximum impact.
| Element | Description | Best practices |
| App icon | Automatically displays your app’s icon | Ensure your app icon is recognizable at small sizes |
| Title | Bold headline text (50 characters visible) | Keep under 25 characters; make it compelling |
| Subtitle | Secondary text below title (iOS only) | Optional; use for additional context |
| Message body | Main notification content (150 characters visible) | Be concise; convey value immediately |
| Rich media | Image, GIF, video, or audio attachment | Use 1:1 aspect ratio; max 10MB |
| Action buttons | Up to 4 interactive buttons | Use clear, action-oriented labels |
| Timestamp | Shows when notification was received | Automatic; consider timing strategy |
Challenges of implementing push notifications
While push notifications are powerful, they come with challenges that require careful management.
| Challenge | Description | Solution |
| Low opt-in rates | Users decline notification permissions | Implement pre-permission prompts; explain value before asking |
| High opt-out rates | Users disable notifications after opting in | Respect frequency limits; ensure relevance |
| Delivery failures | Notifications not reaching devices | Monitor delivery rates; handle invalid tokens |
| Platform fragmentation | Different rules for iOS vs. Android | Use cross-platform services; maintain platform-specific strategies |
| Timing issues | Notifications sent at inappropriate times | Implement send-time optimization; respect time zones |
| Notification fatigue | Users overwhelmed by too many messages | Limit frequency; prioritize quality over quantity |
| Privacy regulations | GDPR, CCPA compliance requirements | Obtain proper consent; provide opt-out options |
| Render rate issues | Android notifications not displaying | Use services with high render rates; handle battery optimization |
Best practices for push notifications
Following proven best practices maximizes the effectiveness of your push notification strategy.
1. Personalize your messages
Generic messages get ignored. Use user data to personalize notifications with names, past behaviors, preferences, and relevant recommendations. Personalized push notifications can achieve up to 4x higher click-through rates than generic messages.
Tips:
- Include the user’s name when appropriate
- Reference past purchases or browsing history
- Tailor offers based on user segments
- Use dynamic content based on user attributes
2. Optimize timing and frequency
Sending notifications at the right time dramatically impacts engagement. Avoid sending during sleep hours or busy periods, and respect time zones for global audiences.
Timing guidelines:
| User context | Best times | Avoid |
| General | 10am-1pm, 7pm-9pm | Before 8am, after 10pm |
| E-commerce | Lunch hours, evening | Early morning, late night |
| News/media | Morning, breaking events | Late night (unless urgent) |
| Gaming | Evening, weekends | Work hours |
| Finance | Business hours | Weekends (unless urgent) |
Frequency recommendations:
- Most apps: 2-5 notifications per week maximum
- High-engagement apps (gaming, social): Up to 1 per day
- Transactional: As needed, but bundle when possible
3. Craft compelling content
Your notification content must immediately convey value and inspire action.
Content checklist:
- Lead with the benefit or value proposition
- Use action-oriented language
- Create urgency when appropriate (without being manipulative)
- Keep messages concise and scannable
- Include clear calls-to-action
4. Use rich media strategically
Images, GIFs, and videos make notifications more engaging and memorable. Rich push notifications can increase engagement by 25% or more.
Rich media best practices:
- Use high-quality, relevant images
- Ensure media loads quickly
- Test across devices for proper rendering
- Consider accessibility (don’t rely solely on images for meaning)
5. Segment your audience
Not all users should receive the same notifications. Segment based on:
- User behavior (active, inactive, purchasers)
- Demographics and preferences
- Lifecycle stage (new, engaged, at-risk)
- Location and timezone
- App usage patterns
6. Provide value, not spam
Every notification should offer genuine value to the user. Ask yourself: “Would I want to receive this notification?”
Value-adding notifications:
- Exclusive offers and early access
- Personalized recommendations
- Timely, relevant information
- Helpful reminders
- Updates on things users care about