Mobile attribution is the process of connecting app installs and in-app actions to specific marketing campaigns, ads, or channels that drove them. It enables marketers to understand which advertising efforts deliver results, optimize ad spend across channels, and make data-driven decisions about user acquisition strategies. With mobile ad spending projected to exceed $400 billion globally, accurate attribution has become essential for maximizing marketing ROI.
What is mobile attribution?
Mobile attribution is the method of identifying which marketing touchpoints—such as ads, campaigns, or channels—lead users to install a mobile app or take specific actions within it. Think of it as detective work that traces a user’s journey from seeing an advertisement to downloading your app and engaging with its features.
When a user clicks on an Instagram ad and subsequently installs your app, mobile attribution tools track this sequence and credit the install to that specific campaign. This tracking extends beyond installs to include post-install events like purchases, sign-ups, subscriptions, and other valuable in-app activities.
Unlike web attribution, which primarily relies on browser cookies, mobile attribution uses device identifiers and Software Development Kits (SDKs) integrated into apps. These SDKs collect data about user interactions and send it to attribution providers, creating a comprehensive picture of marketing effectiveness across the mobile ecosystem.
Mobile attribution vs. web attribution: key differences
| Aspect | Mobile attribution | Web attribution |
| Primary tracking method | Device IDs (IDFA, GAID) + SDKs | Browser cookies |
| Environment | Native apps | Web browsers |
| User identification | Device-level identifiers | Cookie-based identifiers |
| Cross-session tracking | More reliable (device-bound) | Less reliable (cookies can be cleared) |
| Privacy restrictions | ATT, Privacy Sandbox | Third-party cookie deprecation |
| Implementation | SDK integration required | Pixel/tag placement |
| Offline capability | Can track offline conversions | Limited offline tracking |
Why is mobile attribution important?
Mobile attribution is crucial for making informed marketing decisions in an increasingly competitive app marketplace. Without it, you’re essentially flying blind—spending budget without knowing which campaigns actually drive results.
Business impact of mobile attribution
| Benefit | Description | Impact |
| Ad spend optimization | Identifies high-performing channels | 20-40% improvement in ROAS |
| Campaign measurement | Tracks complete user journeys | Accurate ROI calculation |
| User acquisition quality | Reveals which sources bring valuable users | Higher LTV per acquired user |
| Fraud prevention | Detects fake installs and clicks | Protects 10-30% of ad budget |
| Retargeting enablement | Identifies re-engagement opportunities | Improved retention rates |
| Strategic decision-making | Provides data for budget allocation | More efficient marketing spend |
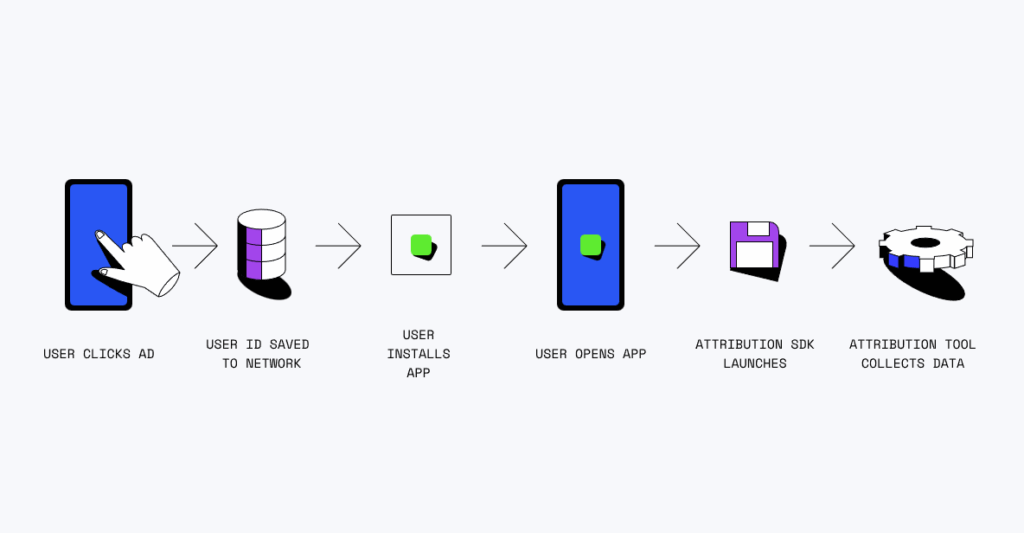
How does mobile attribution work: step by step
Understanding the attribution process helps marketers leverage these tools more effectively. Here’s how mobile attribution works from initial ad interaction to final reporting.
Step 1: User interacts with an ad
The attribution process begins when a user encounters and interacts with a mobile advertisement. This interaction could be clicking a banner ad, watching a video ad, or even just viewing an impression (for view-through attribution). Each interaction creates a “touchpoint” that becomes a data point for tracking.
Step 2: Click and impression data capture
When the user interacts with the ad, the advertising platform captures essential data points including device ID (such as IDFA for iOS or GAID for Android), IP address, user agent information (browser, operating system, device type), and timestamp of the interaction. These identifiers are crucial for matching the user’s journey later in the process.
Data points captured during ad interaction:
| Data point | Purpose | Example |
| Device ID | Unique user identification | IDFA: 6D92078A-8246-4BA4-AE5B-76104861E7DC |
| IP Address | Location and network identification | 192.168.1.1 |
| User Agent | Device and browser information | Mozilla/5.0 (iPhone; CPU iPhone OS 15_0) |
| Timestamp | Interaction timing | 2024-01-15T14:30:00Z |
| Campaign ID | Source campaign identification | campaign_summer_sale_2024 |
| Creative ID | Specific ad creative tracking | creative_video_30s_v2 |
| Publisher ID | Traffic source identification | pub_instagram_feed |
Step 3: Redirect through attribution link
After clicking the ad, the user is redirected through a unique tracking URL containing parameters that identify the ad source, campaign, creative, and other relevant information. This link routes through the attribution provider’s servers before forwarding the user to the appropriate app store.
Step 4: SDK integration captures install
When the user downloads and opens the app for the first time, the attribution SDK integrated into the app captures the install event. The SDK collects device information, install timestamp, and any additional parameters that help match this install to the original ad interaction.
Step 5: Post-install event tracking
The SDK continues monitoring user activity within the app, tracking defined events such as registrations, purchases, subscription starts, level completions, or any other actions you’ve configured. This post-install data is essential for understanding user quality and calculating metrics like LTV.
Step 6: Matching conversion to source
This is where actual attribution occurs. The system matches the install or conversion event back to the original ad interaction using one of two primary methods:
| Method | How it works | Accuracy | When used |
| Deterministic | Exact match of device IDs | ~100% | When IDFA/GAID available |
| Probabilistic | Statistical matching using IP, device type, etc. | 70-90% | When device IDs unavailable |
| Fingerprinting | Device characteristics combination | 60-80% | Privacy-restricted environments |
| SKAdNetwork | Apple’s privacy-preserving framework | Aggregate only | iOS 14.5+ |
Step 7: Attribution window application
The attribution window defines the timeframe during which a user’s ad interaction can be credited for a conversion.
Standard attribution windows by type:
| Attribution type | Typical window | Use case |
| Click-through (short) | 1-7 days | Performance campaigns |
| Click-through (standard) | 7-14 days | Most app install campaigns |
| Click-through (extended) | 14-30 days | High-consideration products |
| View-through | 1-24 hours | Display/video brand campaigns |
| Re-engagement | 1-7 days | Retargeting campaigns |
Step 8: Postback and reporting
Once attribution is determined, the attribution provider sends data back to advertisers and ad networks through postbacks. This information is compiled into detailed reports showing which campaigns, channels, and creatives drove conversions.
Step 9: Optimization and iteration
With attribution data in hand, marketers can optimize campaigns by adjusting budgets toward high-performing channels, refining targeting, testing new creatives, and building retargeting audiences based on user behavior patterns.
7 mobile attribution models
Attribution models determine how credit for conversions is distributed across the various touchpoints a user interacts with. Each model weighs these interactions differently, providing unique insights into marketing effectiveness.
Attribution models comparison
| Model | Credit distribution | Pros | Cons | Best for |
| First-touch | 100% to first interaction | Simple; shows discovery channels | Ignores nurturing touchpoints | Brand awareness campaigns |
| Last-touch | 100% to final interaction | Simple; shows conversion triggers | Ignores awareness efforts | Direct response campaigns |
| Linear | Equal across all touchpoints | Fair distribution; comprehensive | May overvalue minor touchpoints | Multi-channel campaigns |
| Time-decay | More to recent touchpoints | Reflects recency importance | Undervalues awareness | Long sales cycles |
| U-shaped | 40/20/40 (first/middle/last) | Balances awareness and conversion | May undervalue middle funnel | Lead generation |
| W-shaped | 30/30/30/10 (key milestones) | Highlights critical stages | Complex to implement | B2B, milestone-based journeys |
| View-through | Credit for impressions | Measures brand impact | Can overattribute | Display/video campaigns |
1. First-touch attribution
First-touch (or first-click) attribution assigns 100% of credit to the user’s very first interaction with your brand or ad. This model excels at measuring which channels create initial awareness and drive discovery. However, it ignores all subsequent touchpoints that may have influenced the final conversion decision.
2. Last-touch attribution
Last-touch attribution gives all credit to the final touchpoint before conversion. This widely-used model is simple to implement and understand, making it popular for direct response campaigns. However, it overlooks earlier interactions that nurtured the user toward conversion.
3. Multi-touch attribution
Multi-touch attribution (MTA) distributes credit among multiple touchpoints throughout the user journey. Depending on specific rules, credit can be allocated evenly or weighted based on each interaction’s relative importance. MTA provides a holistic view of the customer journey but requires more sophisticated implementation and analysis.
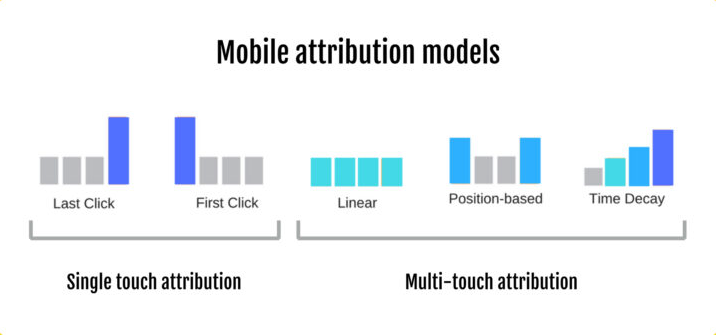
4. Time-decay attribution
Time-decay attribution assigns progressively more credit to touchpoints closer to the conversion, assuming recent interactions are more influential. Earlier touchpoints still receive some credit, but their weight diminishes over time. This model works well for campaigns with longer consideration periods.
5. U-shaped attribution
The U-shaped model gives significant credit to both first and last touchpoints (typically 40% each), with the remaining 20% distributed among middle interactions. This approach emphasizes the importance of both awareness creation and conversion triggers while acknowledging intermediate nurturing.
6. W-shaped attribution
Building on the U-shaped approach, W-shaped attribution adds emphasis to a key middle touchpoint representing a significant milestone—like a demo request or account creation. Typically, 30% credit goes to first, middle milestone, and last touchpoints, with the remainder distributed elsewhere.
7. View-through attribution
View-through attribution credits conversions to ads that users saw but didn’t click. If a user views an ad and later converts through another channel, partial credit goes to the viewed impression. This model is essential for measuring the impact of display and video advertising on brand awareness, even without direct clicks.
How to choose the right mobile attribution model
Selecting the appropriate attribution model depends on your business goals, customer journey complexity, and marketing strategy.
| If your priority is… | Consider this model | Why |
| Understanding discovery channels | First-touch | Shows which channels introduce users to your brand |
| Measuring conversion drivers | Last-touch | Identifies what triggers final action |
| Comprehensive journey analysis | Multi-touch / Linear | Evaluates all touchpoints equally |
| Valuing recent interactions | Time-decay | Gives weight to touchpoints near conversion |
| Balancing awareness + conversion | U-shaped | Emphasizes both ends of journey |
| B2B with long sales cycles | W-shaped | Highlights key milestone touchpoints |
| Measuring brand campaigns | View-through | Credits non-clicked impressions |
Factors to consider when choosing a model
1. Sales cycle length
- Short cycles (< 7 days): Last-touch or first-touch
- Medium cycles (7-30 days): U-shaped or linear
- Long cycles (> 30 days): Time-decay or W-shaped
2. Number of channels
- Single channel: Last-touch sufficient
- 2-3 channels: U-shaped recommended
- 4+ channels: Multi-touch essential
3. Marketing objectives
- Brand awareness: First-touch
- Lead generation: U-shaped
- Direct sales: Last-touch
- Full-funnel optimization: Multi-touch
6 key metrics for mobile attribution
Effective mobile attribution requires tracking specific metrics that reveal campaign performance and user quality.
Essential attribution metrics overview
| Metric | Formula | Good Benchmark | What It Tells You |
| Conversion Rate (CR) | (Conversions / Clicks) × 100% | 1-10% | Ad effectiveness at driving action |
| Click-Through Rate (CTR) | (Clicks / Impressions) × 100% | 0.5-2% | Ad creative relevance |
| Cost Per Install (CPI) | Ad Spend / Installs | $0.50-$3.00 (varies by vertical) | User acquisition efficiency |
| Cost Per Action (CPA) | Ad Spend / Actions | Varies by action type | Quality user acquisition cost |
| Return on Ad Spend (ROAS) | Revenue / Ad Spend | 3:1 or higher | Campaign profitability |
| Lifetime Value (LTV) | Avg Revenue × User Lifespan | Higher than CAC | Long-term user value |
1. Conversion rate (CR)
Conversion rate measures the percentage of users who complete a desired action after interacting with an ad. For app installs, this typically represents installs divided by ad clicks. A good conversion rate for app installs generally ranges from 1% to 10%, depending on the vertical and campaign type.
2. Click-through rate (CTR)
CTR indicates how compelling your ads are to your target audience by measuring the percentage of users who click after seeing an ad. Higher CTR suggests better ad relevance and creative effectiveness. In mobile advertising, CTR above 1% is typically considered decent, though benchmarks vary by industry.
3. Cost per install (CPI)
CPI measures the average cost to acquire one app install through advertising. This metric helps evaluate campaign efficiency and compare performance across channels. Lower CPI indicates more cost-effective user acquisition, though it should be considered alongside user quality metrics.
4. Cost per action (CPA)
CPA goes beyond installs to measure the cost of acquiring users who complete specific valuable actions—subscriptions, purchases, registrations, or other defined events. This metric better reflects actual user value than CPI alone.
5. Return on ad spend (ROAS)
ROAS measures the revenue generated for every dollar spent on advertising. This metric directly connects marketing investment to business outcomes, making it essential for evaluating campaign profitability.
6. Lifetime value (LTV)
LTV estimates the total revenue a user will generate throughout their relationship with your app. When combined with acquisition costs, LTV helps determine which channels deliver the most valuable users, not just the most users.
Challenges in mobile app attribution
Mobile attribution faces several significant challenges that marketers must navigate to maintain accurate measurement.
Common attribution challenges and solutions:
| Challenge | Description | Solution |
| Data discrepancies | Different platforms report different numbers | Use single source of truth (MMP); reconcile regularly |
| Attribution fraud | Fake clicks/installs inflate metrics | Implement fraud detection; work with trusted partners |
| Cross-device tracking | Users interact on multiple devices | Use probabilistic matching; implement user-level IDs |
| Walled gardens | Limited data sharing from major platforms | Accept platform data; focus on owned data |
| SKAdNetwork limitations | Delayed, aggregate data only | Adopt predictive modeling; use conversion value optimization |
| Short attribution windows | May miss delayed conversions | Test longer windows; implement view-through attribution |
Mobile attribution best practices
Following established best practices ensures accurate attribution data and actionable insights.
Implementation checklist
| Task | Priority | Description |
| ✅ Select appropriate MMP | High | Choose based on integrations, fraud protection, reporting needs |
| ✅ Proper SDK integration | High | Verify all events tracked correctly with dev team |
| ✅ Define meaningful events | High | Track events that reflect genuine user value |
| ✅ Implement deep linking | High | Direct users to specific in-app content |
| ✅ Set attribution windows | Medium | Configure windows matching your user journey |
| ✅ Enable fraud protection | High | Activate MMP fraud detection features |
| ✅ Configure postbacks | Medium | Ensure data flows to all platforms correctly |
| ✅ Set up cohort analysis | Medium | Group users for trend analysis |
| ✅ Test multiple models | Low | Compare insights from different attribution models |
| ✅ Regular audits | Ongoing | Verify tracking accuracy monthly |
Top Mobile Measurement Partners (MMPs)
| MMP | Key strengths | Best for | Pricing model |
| AppsFlyer | Market leader; extensive integrations; strong fraud protection | Enterprise apps; gaming | Attribution-based |
| Adjust | Privacy-focused; strong automation; good support | Privacy-conscious brands | Tiered subscription |
| Branch | Deep linking excellence; cross-platform | Apps with complex user journeys | Attribution-based |
| Kochava | Flexible; strong analytics; owned media tracking | Multi-platform marketers | Custom pricing |
| Singular | Cost aggregation; ROI analytics | Performance marketers | Tiered subscription |